Glossary
Terms and abbreviations used on this website:
ADR – Annual Disease Return.
AFB – American foulbrood.
AFB PMP – the American Foulbrood National Pest Management Plan, an official plan under the Biosecurity Act; the AFB PMP uses legislative powers in an effort to eliminate American foulbrood in New Zealand; the NBA is the official Management Agency for the AFB PMP.
American foulbrood – a brood disease of honey bees caused by the bacterium Paenibacillus larvae larvae.
Annual Disease Return – an annual statutory declaration in which a beekeeper confirms and updates apiary location details and reports all cases of AFB found in his/her beehives during the preceding 12 months; part of the AFB PMP and a legal requirement for all beekeepers in New Zealand.
Apiary – a place where beehives are kept; under the AFB PMP, a place where beehives are kept for more than 30 days, providing the place is more than 200 m from any other such place occupied by beehives belonging to the same beekeeper.
Apiary Quarantine – a beekeeping management technique where each apiary is managed separately, without any interchange of equipment between apiaries; used to reduce the spread of AFB.
Approved Beekeeper – a beekeeper with a DECA; part of the AFB PMP.
Area Quarantine – a beekeeping management technique where apiaries in a certain area are managed as a unit, without any interchange of equipment with other units; used to reduce the spread of AFB.
Beehive – the supers, bottom board and other equipment used together to contain a honey bee colony; under the AFB PMP, an object that has been constructed for the keeping of honey bees and is either being used for that purpose, or has in the past been used for that purpose.
Biosecurity Act – an Act of Parliament used to implement the AFB PMP.
Bottom Board – a specially constructed board that the supers sit on; creates an entrance that the bees use to exit and enter the hive.
Brood – honey bees in the developmental stages (eggs, larvae and pupae) before the adult stage.
Brood Box – box or super used to contain brood combs; the queen bee is usually confined to the brood box (see super).
Capped Brood – brood in the prepupal or pupal stage after adult bees have sealed over the cells containing the brood with cappings.
Cappings – the wax covering adult bees put over a cell containing a larva before the larva pupates; also the wax covering that bees put over cells once the cells have become full with honey.
Certificate of Inspection – an annual statutory declaration that hives owned by a person without a DECA have been inspected for AFB by an Approved Beekeeper; part of the AFB PMP.
Chalkbrood – a disease caused by the fungus Ascosphaera apis that affects honey bee brood.
C of I – Certificate of Inspection.
Colony – a colony of honey bees.
Commercial Beekeeper – a beekeeper who makes a full-time living from beekeeping.
Composite Samples – a combined sample of bees taken from a number of beehives; collected for analysis using the culture test.
Contaminated Colony – a honey bee colony that has spores of AFB that can be seen by the Beekeeper, but doesn’t produce diseased larvae or pupae
Culture Test – a laboratory test where washings of bees or dilutions of honey are put onto an agar plate and incubated to encourage the germination of AFB spores and the growth of AFB bacterial colonies.
Disease Elimination Conformity Agreement – a document signed with the Management Agency in which an Approved Beekeeper details a plan for detecting and eliminating AFB within his/her own beehives; a voluntary component of the AFB PMP.
DECA – Disease Elimination Conformity Agreement.
Diseaseathon – an organised programme of voluntary AFB inspections.
Division Board – a thin board with rims that is used to divide a beehive into halves; used for making tops; division boards are also often used as hive mats.
Dump Site – a place where beehives are brought together, either just before or just after they are used in an orchard for pollination.
Drawn Comb – a frame that the bees have built out with comb; usually means empty comb.
Drift – the returning of bees to the wrong hive.
EFB – European foulbrood.
European foulbrood – a brood disease of honey bees caused by the bacterium Melissococcus plutonius.
Extraction; Extractor – the process of removing honey from frames, using a machine that applies centrifugal force to the frames (called an “extractor”).
Feed Honey – combs containing honey that a beekeeper retains over winter and puts back into hives in the spring.
Feral Colonies – colonies of honey bees that exist in the wild and are not kept by man.
Foundation – thin, purpose-made beeswax sheets imprinted with a hexagonal pattern; foundation is put into frames and then placed in the beehive where the bees build wax comb on top of the foundation (called “drawing out”). May also be made of plastic which beekeepers may brush with melted beeswax.
Frame – the wooden surround of a comb found in a beehive; also the entire structure (wood and comb). May also be made of plastic.
Half-moon Syndrome – a disorder of honey bees with characteristics closely resembling the symptoms of EFB; does not appear to be a disease of honey bees, since no organism has ever been found that produces the syndrome’s effects.
Hive Mat – a cover underneath the weather-proof lid of the beehive; usually made either of plastic sacking, plywood or particle board.
Hive Quarantine – a beekeeping management technique where each honey bee colony is managed by itself, with no interchange of equipment between hives; used to control the spread of AFB.
Hive Tool – a purpose-built lever and scraper used by beekeepers to pry apart supers and help remove frames.
Hobbyist – a beekeeper who doesn’t keep bees for a living.
Honey Super – a super and frames used mainly or only during the honey production part of the year; honey supers are removed when they are full and are taken back to the beekeeper’s shed to be extracted and stored.
Hygienic Behaviour – the uncapping and removal of dead larvae and pupae by adult bees.
Inapparent Infection – a subclinical or non visible infection of AFB.
Incidence of AFB – the number of honey bee colonies found with AFB compared with the total number of colonies in a population; AFB incidence is often calculated on an annual basis.
Larva – (plural: larvae) – the middle developmental stage of a honey bee; the stage is 5 days in duration, and is the period during which brood becomes infected with AFB.
Laying Workers – an abnormality caused when the colony loses its queen and another queen is not produced; worker bees develop their rudimentary ovaries and begin laying unfertilised eggs which become drones; results in many eggs being laid in each cell.
Lid – the weather-proof cover and top of a beehive.
Management Agency – an organisation that administers and carries out a Pest Management Plan under the Biosecurity Act; in the case of the AFB PMP, the NBA.
Mummies – the dried down remains of larvae infected with chalkbrood.
NBA – the National Beekeepers’ Association.
NBA Ward– a formalised grouping of NBA members in a designated geographic area.
National Beekeepers’ Association – the representative body of the beekeeping industry in New Zealand, and the Management Agency for the AFB PMP.
Nuc, Nucleus – a small beehive, generally consisting of 4 frames, in a purpose-built super (called a “nuc box”); nucs are often used in queen rearing (called “mating nucs”).
Outbreak – a situation in which AFB is found in much higher than normal levels in an apiary or beekeeping outfit.
Package Bees – a broodless nucleus colony, comprised of a caged queen and an artificial swarm of bees in a screened shipping carton.
Paenibacillus larvae – the bacterium that causes AFB; until recently the bacterium was known as Bacillus larvae, but scientists have now determined that the organism should be in its own unique genus (Paenibacillus).
Pollen Mites – tiny scavenger mites that feed on pollen in stored combs; produce a fine powder of pollen that covers cell walls and fall to the bottom of stacks of stored supers.
Prepupa – a larva laying out along the bottom wall of a cell before pupation; AFB symptoms can first be identified at this stage.
Pupa – (plural: pupae) – the final stage of development of the honey bee; the stage when brood take on the adult form before emerging as an adult bee; AFB symptoms can be found at both the pupal and prepupal stages.
Pupates; Pupation – the process of change from a larva into a pupa.
Quarantine – the isolation of things that might carry a disease so that the disease will not have the chance to spread.
Queen Cell – a specially built cell the bees produce that holds a developing queen bee; also the wax cell either before or after it holds a developing queen.
Queen Excluder – a purpose-built device made of small wire grids that are small enough not to allow a queen to pass through, but which do not restrict worker bees; used to keep a queen from laying in honey supers.
Queen, Failing – a queen that, as a result of old age or lack of retained semen, slows down her egg laying rate and begins to lay drone eggs in worker cells.
Queen Rearing – the production of queen cells through the use of beekeeping management techniques; also the production of mated queens.
Registration Number; Beekeeper Registration Number – a unique number issued to a beekeeper by the Management Agency when the beekeeper first registers an apiary; often branded on supers or frames as a means of identification; required to be displayed in an apiary.
Re-queening – the removal of the queen in a beehive by a beekeeper, and the replacement with a new queen or in some cases a queen cell.
Robbing – foraging honey bees from one hive taking honey from another; a strong behavioural response by bees that is often difficult for the beekeeper to control.
Ropiness; Ropiness Test – characteristic stringing of diseased larval or pupal tissue when the tissue is slightly stirred with a stick and then slowly removed; the ropiness test is used as a field diagnosis for AFB.
Sacbrood – a viral disease affecting honey bee brood; some symptoms of sacbrood closely resemble AFB.
Scale – the dried remains of brood that lie flat along the lower wall of the cell; commonly found in association with AFB, but also sometimes present in sacbrood, EFB and half-moon disorder.
Semi-Commercial Beekeeper – a beekeeper who doesn’t make a full-time living from beekeeping.
Shook Swarming – a method of AFB control used in the past in New Zealand; bees were shaken from infected hives into hives that contained only foundation; while the method was at times effective at eliminating the disease, painstaking effort was required, and some hives still developed heavy infections and had to be destroyed.
Site Book – a diary used by beekeepers to record management operations in individual apiaries.
Smoker – a purpose-built device comprising of a metal canister and bellows; used to blow smoke onto bees when the beekeeper is working a hive; the smoke has a calming effect on the bees and also moves the bees away from the area where the smoke is blown.
Split – the creation of a new beehive using bees, brood frames and honey frames from one or more hives (often called “parent hives”); the split is usually given a new mated queen or a queen cell. See Top.
Spore; Spore Form – the bacterial stage at which AFB spreads within the hive and from one hive to another; AFB spores have a remarkably hard outer coat that protects their germplasm contents from destructive forces.
Spotty Brood Pattern – a frame of mostly capped brood where many of the cells are not capped; normally, queens lay eggs of similar age in close proximity, resulting in almost all cells being capped at the same time. Caused by failing queen, disease, or chilling.
Subclinical Infection – an infection of AFB where no visual symptoms appear in the colony.
Super – the box that holds frames; also the box and the frames together; supers are put one on top of another (“superimposed”) in order to make a beehive.
Swarm – a large number of honey bees, including a queen, that have left their parent colony to establish a new colony elsewhere; the natural means of colony multiplication, and dispersal.
Top – a split that is kept on top of the parent colony above a division board.
Vegetative Stage; Vegetative Rods – the bacterial stage at which AFB grows inside a larva or pupa.
Wax Dipping; Paraffin Dipping; Dipping – the sterilisation of beekeeping woodenware by emersion for at least 10 minutes in paraffin wax heated to above160°C; kills AFB spores.
Wet Honey Supers; Wets or Stickies – honey supers after the frames have been extracted; called “wets” because a residue of honey remains on the combs.
Take the AFB 5 minute quiz
How well do you know what you need to know about AFB and beekeeping? Take our short quiz and find out.
Videos
Our videos cover everything from your legal obligations to how to recognise AFB, collecting cell and bee samples and more.
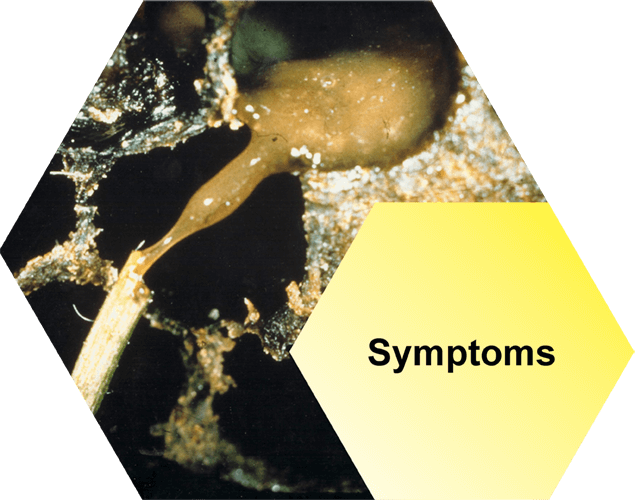
Symptoms
There’s a lot of good information here, telling you everything you need to know about recognising AFB: the visual symptoms, smell of AFB and more.
Inspection and Diagnosis
Successfully eliminate AFB by telling the difference between symptoms of AFB and other brood diseases in the hive. We tell you the best methods for inspecting your hives.
The Law
New Zealand beekeepers have a number of legal obligations that must be met regarding AFB disease. Read the shortened list in summary, here.
Elimination
Most hives become infected because bees, honey or equipment have been put into a hive from another hive that is infected with AFB. Lower your chances of an AFB infection by reading this section.
AFB Recognition Course Info
Find out when the next AFB Recognition and Competency Courses, or Refresher Courses are available. These are held throughout the year in various New Zealand locations across the South Island and North Island.
The AFB App
Follow the link below to open the App. Once open to save to your device you need to bookmark the URL on your phone so you can find it easily again. Please click here to open.