Differences between common diseases
Table 2 compares the distinguishing features of AFB and the other brood diseases and abnormalities.
Table 2: Distinguishing features of honey bee brood diseases and disorders
| Brood comb appearance | Age of dead brood | Colour and shape of dead brood | Consistency of dead brood | Odour of brood | Dried remains (scale) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| American foulbrood | Normal cell cappings, sunken dark, perforated cappings, or cappings completely removed | Prepupae or young pupae | Off white, then coffee brown, then black. Even coloured. Lose segmented outline | Smooth rope 10-30mm. Elastic thread “snap back” when breaks. Difficult to remove larval remains | Like dead fish | On bottom side of cell, hard to remove, pupal tongue can often be seen |
| Sacbrood | Cappings same as AFB | Prepupae only | Grey or yelow then brown, sometimes with a grey or black head. Segmented outline present | Plastic sac, watery contents of sac often lumpy. Sometimes ropes to small extent. Prepupae easily removed from the cell | Slightly sour | Dark brown, easily removed in one piece. No tongue but prepupal head may be curled up. Scales not common, except in severe infections |
| Chalkbood | Cappings same as AFB | Prepupae only | White (often with a yellow head), or black | Soft, furry, filling cells, hexagonal shape. Later shrinking to hard chalky mummies | Not noticeable | White or black, hard, easily removed mummies |
| Parasitic mite syndrome | Cappings same as AFB | Older larvae and prepupae (not pupae) | White, grey or yellow. Dried remains may be orange | Watery, pasty; does not rope; dries to scale. Presence of varroa sometimes observed | Sometimes sour urine-like | Twisted up the wall of the cell. Sometimes curled around the entrance. Easily removed from cell. No tongue present |
| Half-moon syndrome | Cappings same as AFB. Multiple eggs in cells, eggs attached in chains, and sometimes drone brood in worker cells | Young larvae to older sealed larva | Off white to dark brown. Trachea may be seen as dark lines in larvae | Watery, pasty; does not rope | Sour urine-like | Twisted up the wall of the cell. Sometimes curled around the entrance. Easiliy removed from cell. No tongue present |
Take the AFB 5 minute quiz
How well do you know what you need to know about AFB and beekeeping? Take our short quiz and find out.
Videos
Our videos cover everything from your legal obligations to how to recognise AFB, collecting cell and bee samples and more.
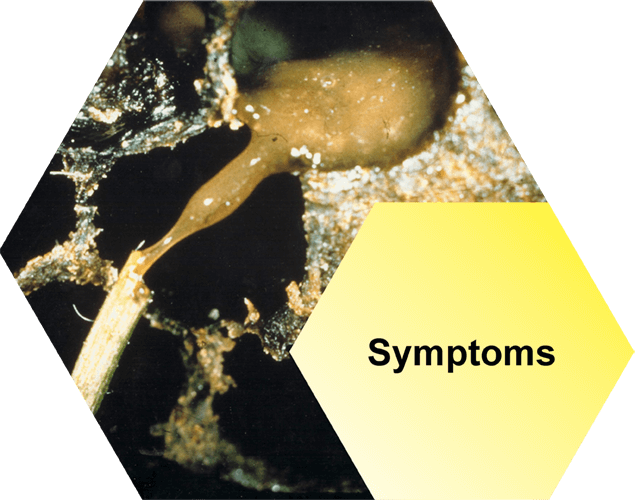
Symptoms
There’s a lot of good information here, telling you everything you need to know about recognising AFB: the visual symptoms, smell of AFB and more.
Inspection and Diagnosis
Successfully eliminate AFB by telling the difference between symptoms of AFB and other brood diseases in the hive. We tell you the best methods for inspecting your hives.
The Law
New Zealand beekeepers have a number of legal obligations that must be met regarding AFB disease. Read the shortened list in summary, here.
Elimination
Most hives become infected because bees, honey or equipment have been put into a hive from another hive that is infected with AFB. Lower your chances of an AFB infection by reading this section.
AFB Recognition Course Info
Find out when the next AFB Recognition and Competency Courses, or Refresher Courses are available. These are held throughout the year in various New Zealand locations across the South Island and North Island.
The AFB App
Follow the link below to open the App. Once open to save to your device you need to bookmark the URL on your phone so you can find it easily again. Please click here to open.